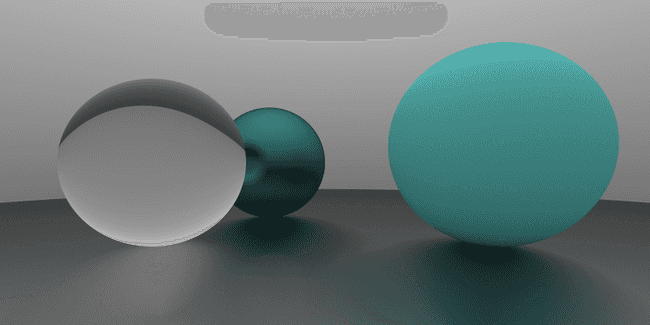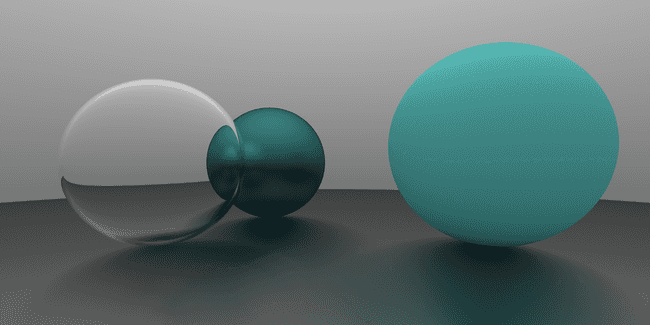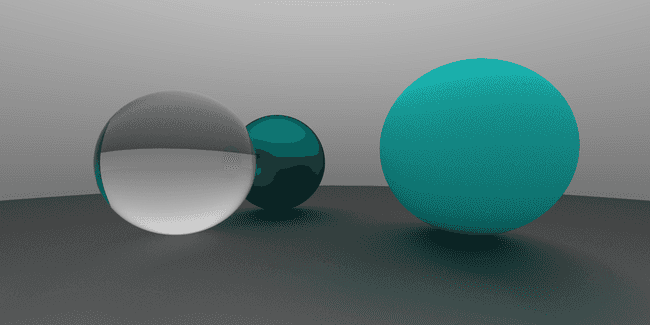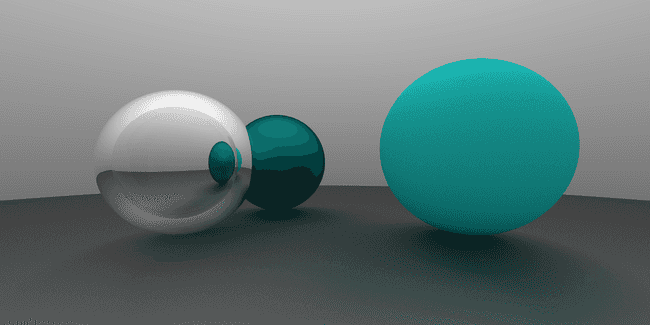两天实现光线追踪 4 - 折射
by acdzh · 2020年12月31日8:4 · 71 WORDS · ~ 1 mins reading time · 0 Visitors |
折射
斯涅尔定律
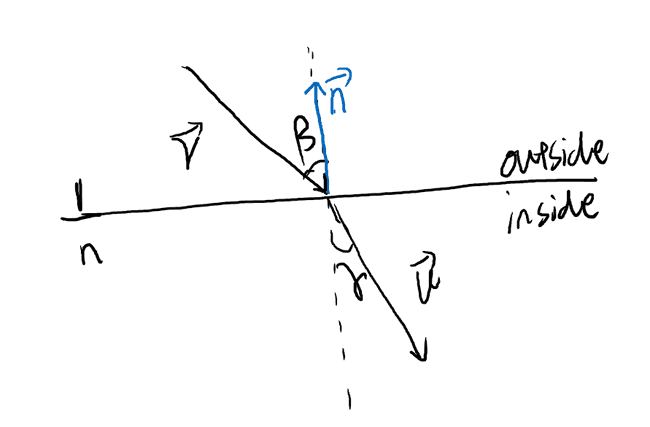
我们需要一个折射函数, 入参为入射光线方向向量 和法线向量 , 以及材质的折射率.
折射率 .
我们有 .
即 .
那么 , 满足 时, 才会发生折射.
下面我们求出射光线方向 . 设 , 在法线上的投影分别为 和 , 在切线上的投影分别为 和 , 显然有 , .
, 以及 , 即 .
那么 .
函数如下
const refract = (v: Vec3, n: Vec3, refractivity: number) => {const vDotN = Vec3.dot(v, n);const cos2γ = 1.0 - (1 - vDotN ** 2) * refractivity ** 2;if (cos2γ < 0) {return null;} else {return v.sub(n.mul(vDotN)).mul(refractivity).sub(n.mul(Math.sqrt(cos2γ)));}};
对于折射率, 光线离开物体时折射率需取倒数. Ray 中的折射函数实现如下, 当不发生折射时就进行反射.
refract(hit: HitRecord, refractivity: number) {const { normal } = hit;const isRayGoOut = Vec3.dot(this.direction, normal) > 0;const res = refract(this.direction,isRayGoOut ? normal.mul(-1) : normal,isRayGoOut ? refractivity : 1 / refractivity);if (res) {return new Ray(hit.p, res);} else {return this.reflect(hit);}}
新建一个透明材质 Dielectric.
export default class Dielectric implements Material {albedo: Vec3;refractivity: number;constructor(albedo: Vec3 | number, refractivity: number) {this.albedo = new Vec3(0, 0, 0).add(albedo);this.refractivity = refractivity;}scatter(rayIn: Ray, hit: HitRecord): [Ray, Attenuation] {return [rayIn.refract(hit, this.refractivity), this.albedo];}}
给最左边的球换上新材质
new Sphere(new Vec3(-1, 0, -1), 0.5, new Dielectric(new Vec3(1, 1, 1), 1.8))
当折射率为 0.7 时, 效果如下
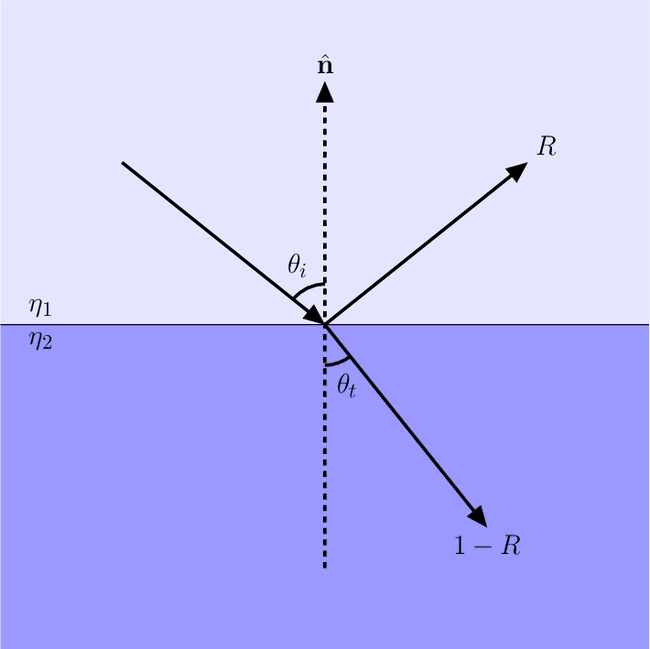
菲涅耳方程
实际上, 即使不发生全反射, 仍然会有部分光线发生反射. 菲涅尔方程描述了此时折射强度与反射强度的关系. 如下图所示, 反射比为 , 折射比为 ,
对于电介质而言, 有如下方程
和 分别表示入射光的 s 偏振和 p 偏振的反射比. 一般情况下, 不考虑偏振时, 我们认为入射光的反射比
这个方程可以使用菲涅耳-施里克近似法进行近似:
https://learnopengl.com/PBR/Theory Fresnel equation节
const schlick = (cosine: number, refractivity: number): number => {const r0 = ((1 - refractivity) / (1 + refractivity)) ** 2;return r0 + (1 + r0) * (1 - cosine) ** 5;};
更新折射方法
refract(hit: HitRecord, refractivity: number) {const { normal } = hit;const isRayGoOut = Vec3.dot(this.direction, normal) > 0;const consine = isRayGoOut ?refractivity * Vec3.dot(this.direction, hit.normal) :-1 * Vec3.dot(this.direction, hit.normal);const res = refract(this.direction,isRayGoOut ? normal.mul(-1) : normal,isRayGoOut ? refractivity : 1 / refractivity);if (res && Math.random() > schlick(consine, refractivity)) {return new Ray(hit.p, res);} else {return this.reflect(hit);}}
效果如下, 注意透明球的右侧的绿色反光. (后来发现这里有错误, 这两张图是在后面更新摄像机实现后重新渲染的, 因此视角与前面稍有不一致)
当折射率为 0.7 时, 效果如下
历史记录
| Version | Action | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | Init | 2021-03-18 16:44:19 |
| 1.1 | 修正菲涅耳方程效果示意图 | 2021-03-23 17:34:31 |